Aim
To study different types of plant tissues under a microscope and understand their structure and function.
Materials Required
- Microscope
- Glass slide
- Cover slip
- Water
- Leaf peel (e.g., Rhoeo leaf or Tradescantia leaf for epidermal tissue study)
- Stain (safranin or iodine solution for better visibility of tissues)
Image Reference
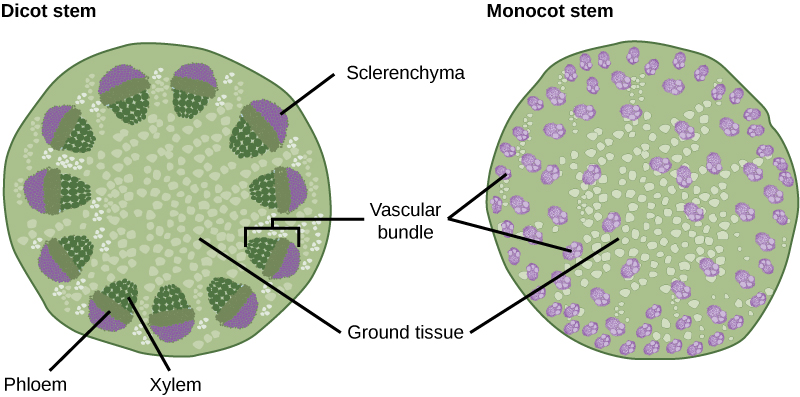
Procedure
- Using forceps, peel a thin layer from the lower epidermis of a leaf (e.g., Rhoeo or Tradescantia leaf).
- Place the peel in a drop of water on a clean glass slide to prevent it from drying out.
- Add a drop of stain (e.g., safranin) to the peel and allow it to sit for 1-2 minutes to enhance the visibility of cell structures.
- Gently place a cover slip over the sample to avoid trapping air bubbles.
- Place the slide under the microscope. Begin with the lowest magnification lens to locate the tissues, then switch to higher magnifications for a detailed view.
- Observe the different types of tissues like the epidermis, stomata, xylem, and phloem in the leaf peel.
Observation
Under the microscope, the following tissues can be identified:
- Epidermis: A single layer of cells forming the outermost boundary of the leaf. The cells are rectangular and tightly packed.
- Stomata: Small openings in the epidermis surrounded by guard cells that regulate gas exchange.
- Xylem: Vascular tissue responsible for the transport of water and minerals. Appears as thick-walled, tube-like cells.
- Phloem: Vascular tissue that transports food. Consists of thin-walled cells adjacent to the xylem.
Inference
This experiment highlights the presence and functions of different plant tissues:
- Epidermis: Protects the leaf and prevents water loss.
- Stomata: Facilitates gas exchange and transpiration.
- Xylem and Phloem: Part of the vascular system, transporting water, minerals, and food throughout the plant.
Video Reference
Experiment Progress
Progress: 0%
Knowledge Check
Question 1:
What is the main function of stomata in plant tissues?
Question 2:
Which of these plant tissues is responsible for the transport of water and minerals?