Aim
To study the effect of concentration on the rate of reaction between hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sodium thiosulphate (Na₂S₂O₃).
Materials Required
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
- Sodium thiosulphate (Na₂S₂O₃)
- Water bath
- Conical flask
- Measuring cylinder
Image Reference
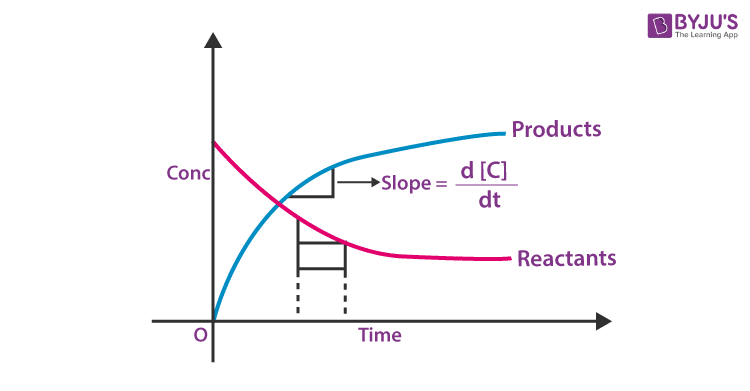
Procedure
- Take a conical flask and add a known concentration of sodium thiosulphate solution.
- Add hydrochloric acid (HCl) to the flask and immediately start the stopwatch.
- Place the flask in a water bath at a constant temperature.
- Observe the reaction as the solution turns cloudy due to the formation of sulfur. The time taken for the solution to become opaque will be recorded.
- Repeat the experiment with varying concentrations of sodium thiosulphate to observe how the reaction rate changes with concentration.
Observation
The reaction rate increases with an increase in the concentration of sodium thiosulphate. A higher concentration leads to a faster rate of reaction, demonstrated by the quicker formation of a cloudy precipitate.
Reaction Equation
Na₂S₂O₃ (aq) + 2HCl (aq) → 2NaCl (aq) + H₂O (l) + SO₂ (g) + S (s)
Precautions
- Ensure to use the same volume of hydrochloric acid and sodium thiosulphate for each trial.
- Perform the experiment at a constant temperature using the water bath to avoid temperature fluctuations.
- Wear safety goggles and gloves while handling acids and chemicals.