Aim
To study the chemical properties of acids when they react with metals and bases, and to understand the formation of hydrogen gas during acid-metal reactions and the neutralization reaction between acids and bases.
Materials Required
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
- Zinc metal (Zn)
- Sodium hydroxide solution (NaOH)
- Litmus paper (red and blue)
- Test tube
- Test tube holder
Image Reference
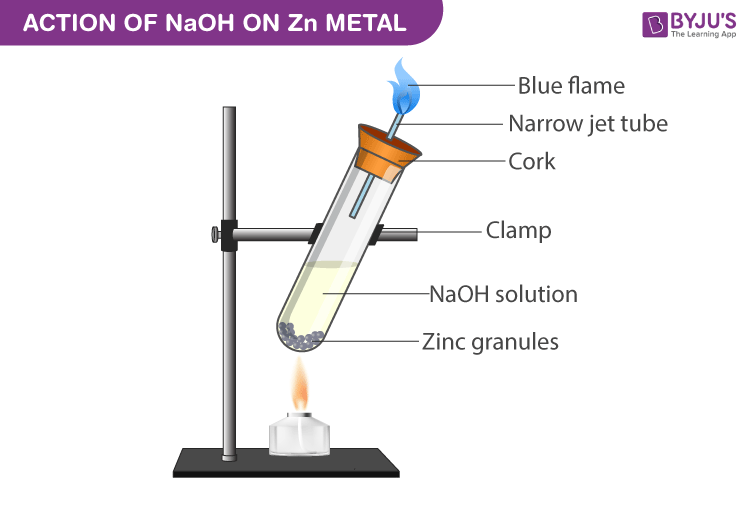
Procedure
- Take a clean test tube and place a small strip of zinc metal in it. Zinc is a reactive metal and will react with hydrochloric acid to produce hydrogen gas.
- Carefully add a few drops of dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl) to the test tube containing zinc. Ensure that the zinc strip is fully submerged in the acid.
- Observe the reaction. You will notice effervescence (bubbles) indicating the release of hydrogen gas. Test the gas by bringing a burning matchstick near the mouth of the test tube. If it extinguishes with a characteristic 'pop' sound, it confirms the presence of hydrogen gas.
- Now, take another clean test tube and pour a few drops of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solution into it. Sodium hydroxide is a strong base and can neutralize an acid.
- Test the nature of the NaOH solution using both red and blue litmus paper. The red litmus paper should turn blue, confirming the basic nature of the solution.
- Gradually add hydrochloric acid (HCl) to the NaOH solution drop by drop. Continuously test the mixture with litmus paper. You will observe the litmus paper turning neutral, indicating that the base has been neutralized by the acid.
Observation
1. Acids react with metals like zinc to produce hydrogen gas, as evidenced by the effervescence and the 'pop' sound.
2. Acids neutralize bases (like NaOH), forming water and a salt, as seen in the change in color of litmus paper and the neutralization of the base.
Reaction Equations
- Reaction with metal:
Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2↑(Zinc reacts with hydrochloric acid to form zinc chloride and hydrogen gas.) - Neutralization reaction:
NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O(Sodium hydroxide reacts with hydrochloric acid to form sodium chloride and water.)
Precautions
- Handle acids and bases with care as they are corrosive and can cause burns. Always wear protective gear like gloves and goggles.
- Ensure that the experiment is conducted in a well-ventilated area to avoid the accumulation of gases.
- Dispose of the chemicals properly after the experiment, following safety protocols.
Video Reference
Quiz
Progress: 0%
1. When acids react with metals, which gas is produced?
2. What is formed when an acid reacts with a base?