Aim
To observe and understand the neutralization reaction between an acid and a base, and to learn how an indicator helps in detecting the endpoint of the reaction.
Materials Required
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
- Sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
- Phenolphthalein solution (indicator)
- Beaker
- Burette
- Stirring rod
Image Reference
Procedure
- Take a few drops of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solution in a clean beaker. NaOH is a strong base and will help in observing the neutralization process.
- Add a few drops of phenolphthalein indicator to the NaOH solution. The solution will turn pink because phenolphthalein is pink in an alkaline medium.
- Fill a burette with hydrochloric acid (HCl) solution. HCl is a strong acid that will neutralize the base.
- Slowly add HCl from the burette to the NaOH solution in the beaker while stirring the mixture gently with a stirring rod. The acid will neutralize the base gradually.
- Continue adding HCl drop by drop until the pink color fades and the solution becomes colorless. This color change indicates that the neutralization reaction is complete, meaning the acid has fully neutralized the base.
Observation
The acid (HCl) reacts with the base (NaOH), and the color change from pink to colorless indicates that the neutralization point has been reached. The reaction between the acid and base forms salt and water, and the pink color fades as the solution becomes neutral.
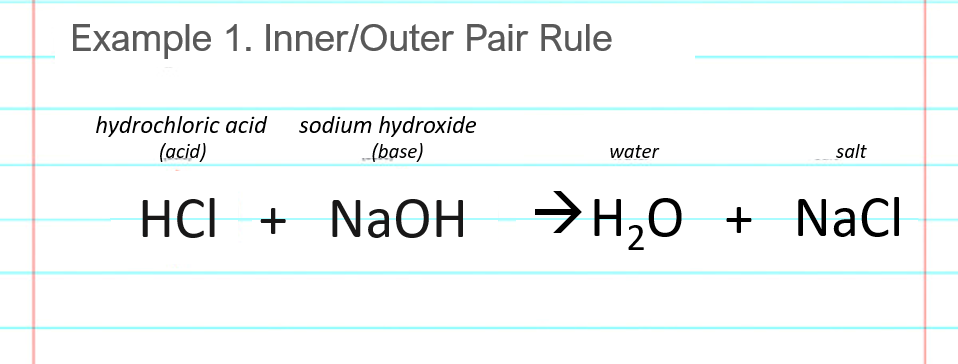
Reaction Equation
NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O
This reaction shows the neutralization of a strong base (sodium hydroxide) by a strong acid (hydrochloric acid) to form water and sodium chloride (a neutral salt).
Precautions
- Handle acids and bases with caution as they are corrosive and can cause burns. Always wear gloves and safety goggles.
- Ensure that the burette is properly cleaned before use to avoid contamination of the reagents.
- Perform the experiment slowly and carefully, adding HCl drop by drop to avoid overshooting the neutralization point.
- Dispose of the chemicals safely after the experiment, following safety guidelines.
Video Reference
Quiz
Progress: 0%
1. What color does phenolphthalein turn in a basic solution?
2. The product of acid-base neutralization is: