Aim
To verify Ohm's law, which states that the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage across it, provided the temperature remains constant.
Materials Required
- Resistor (with known resistance)
- Ammeter (for measuring current)
- Voltmeter (for measuring voltage)
- Battery (with adjustable voltage, e.g., variable power supply)
- Connecting wires
- Rheostat (optional, to vary current)
- Switch
Image Reference
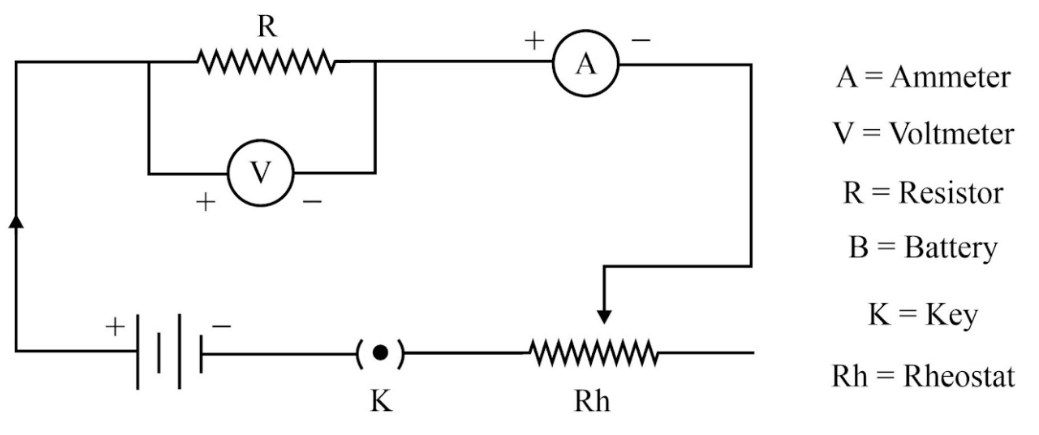
Procedure
- Set up the circuit by connecting the resistor, ammeter, and voltmeter in series and parallel as required. Ensure that the battery and switch are correctly placed for controlling the circuit.
- Turn on the power and measure the voltage across the resistor using the voltmeter and the current passing through the resistor using the ammeter. Record these values.
- Vary the voltage by adjusting the battery or using a rheostat to change the current. For each change in voltage, measure the corresponding current through the resistor.
- Repeat the measurements for at least five different voltage values.
- Plot a graph of voltage (Y-axis) vs. current (X-axis). The resulting graph should be a straight line through the origin if Ohm's law holds true.
Observation
The graph of voltage vs. current is a straight line, indicating that the current is directly proportional to the voltage. This confirms Ohm’s law, where the resistance (R) remains constant and the ratio of voltage to current (V/I) equals the resistance.
Precautions
- Ensure that the ammeter and voltmeter are connected correctly in the circuit: the ammeter in series and the voltmeter in parallel with the resistor.
- Use a variable power supply or rheostat to gradually change the voltage, preventing sudden surges in current.
- Ensure that the resistor does not overheat, as it could affect the results by changing its resistance with temperature.
- Take accurate readings from the ammeter and voltmeter, noting their units.
Conclusion
The experiment verifies Ohm's law, which states that the current through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage across it, provided the temperature is constant. This is observed in the straight-line graph plotted between voltage and current.